|
Need more info or you couldn't find what you were looking for, let us know by sending an email to: support@dancik.com.
Navigator Product Line File
The Product Line File links the items within a manufacturer into groups that are usually defined by the manufacturer. Product lines should be, whenever possible, set up to reflect the product lines that appear in a manufacturer’s catalog. The Product Line File also contains important purchasing parameters that can apply to all items within the product line. For natural products such as marble and stone, the manufacturer code and product line codes represent groups and categories as opposed to actual brand name product lines.
To create a new Product Line File, click Records and then select Create.
|
Field Name |
Description/Instructions |
Manufacturer |
The Manufacturer of the product line you want to inquire about, update or add. The manufacturer must have been previously entered in the Manufacturer File. |
Product Line |
The product line number should be the first three letters of the product line name, or a three-character abbreviation. |
Name |
Name or description of the product line. For example, Bright Glaze Wall Tile, Italian Marble Slabs, Natural Parquet Flooring, or Super Stick Adhesives. Whenever possible, we recommend that you use the manufacturer’s actual product line name. |
UM |
Unit of measure in which the products within this product line are usually sold. This unit of measure does not prevent the individual items in this product line from being sold in other units of measure. |
Consignment Only |
Enter Y if the product line contains only items which are stocked on a consignment basis from the supplier. Otherwise, leave blank. Consignment items can be separately analyzed on inventory analysis and sales reports. |
Lead Time Days |
Average number of days between placing a purchase order for items in this product line and receiving the items. Item File lead time overrides the Product Line File lead time. |
Order Frequency Days |
Frequency, in days, that the product line is ordered or reviewed for the purpose of ordering from the supplier. If you enter the lead time and the order frequency, and blank out the other control parameters (weeks to stock, reorder point, and reorder amount), the program displays default reorder control parameters based on standard reordering formulas. In order to achieve “Just in time” inventory reordering, the order frequency should represent the frequency of incoming shipments. For example, even with a lead time of 30 days, if this product is included on incoming shipments every ten days, then the order frequency is 10. |
Days to Stock |
Optimum number of days to stock. The computer then figures the actual unit quantity to stock by multiplying the average weekly usage of each item by the number of weeks entered here. This entry allows the quantity to stock to shift with demand. |
Reorder Point Days |
Enter quantity, expressed in days of demand, below which a reorder should be generated. |
Safety Stock |
Safety Stock = (Days to stock) - (Order Frequency Days). This field is not input capable. Safety Stock is the days of stock in excess of the minimum possible requirement, which is order frequency. Safety Stock should be set considering shade requirements, normal job sizes and fluctuations in supply and demand. If Safety Stock is negative, it displays in red. Negative Safety Stock means that your days to stock does not even support your minimum requirements. |
Reorder Amount Days |
Quantity, expressed in days of demand, that should be reordered when the reorder point is reached. |
Targeted Turns Days |
Targeted Turns is the number of inventory turns that would result if the reorder parameters were followed exactly as stated. Targeted Turns is input capable. If you enter Targeted Turns, the Days to Stock will be recalculated to coincide with that number of turns. |
Reorder/Buying Category |
Three-character code representing the buyer or the buying category. It is used to group products on the reorder reports. These codes must first be set up in the Classification Codes File. |
Lost MTD |
This field cannot be updated. It displays the total month-to-date order quantity that was lost. Lost is defined as being invoiced for less quantity than was ordered. Large quantities in this field can indicate that inventory counts are incorrect, or back orders are not being filled promptly. This quantity is the cumulative difference between the quantity ordered column and the quantity shipped column of all monthly invoices for this product line. |
Terms |
One-character payment terms code, if payment terms to your customers are based on products. If your payment terms are assigned to customers, covering all products, you do not need to enter a code in this field. To initiate terms by product, follow these guidelines:
|
Terms% and Days |
If your payment terms are by product, then you can use the terms code fields, or these fields. You can enter a percentage discount as well as number of days until due. For example, 2%, 30 days indicates 2% discount if paid within 30 days. |
Direct Ship Terms Code |
If different terms are to be applied for direct ships, enter that terms code here. Terms codes are established in the Payment Terms File. |
Unique Serial |
If you enter Y to generate unique serial numbers, the Receipts and Back Order Fill System (option 6 on the Inventory Control Menu) automatically assigns a unique six-digit serial number each time a receipt is entered. |
Default serial# |
If you enter a default serial number here, the Receipts and Back Order Fill System (option 6 from the Inventory Control Menu) automatically inserts that serial number for each receipt of this product. |
Serial number: Prefix: Suffix: |
These fields allow you to assign a one or two character prefix and suffix to serial numbers automatically generated during the receiving process. Unique serial numbers can aid in identification of inventory transactions, and improve bar code scanning processes. These fields along with the field Generate Unique Serial Numbers work in conjunction with the receiving application (INB 1) to assign unique serial numbers to inventory at time of receipt. For more information, refer to the Inventory Management Reference. For example if the Prefix is set to A and the Suffix is set to R, unique serial numbers will be generated for all inventory receipts of products from this manufacturer, and those serial numbers will be generated in the following format: AnnnnnnR - Where nnnnnn represents a unique six-digit number. This format will apply to all products in this product line, these settings override settings made in the Manufacturer File. |
Default/Unique Serial# Qualifier |
Qualifies how the unique and default serial numbers work. Blank - If left blank the unique serial number generation or default serial number applies to all items within the product line.
The Receiving Program (pre-receipts only) shows the default serial number as usual, except as follows:
|
D/Del |
Enter a D in this field to delete this record. |
These options are available on the Update Record window.
Reorder Parameters by Warehouse
|
The Product Line Notepad Screen screen allows you to enter additional information regarding the Product Line.
|
Special Instructions on Printed Documents
Use this screen to enter special instructions for this Product Line and to note instructions that should be printed on an invoice, pick list, purchase order, order acknowledgement, or quotation.
|
Field Name |
Description/Instructions |
Main Type |
Use this field to categorize each line of text. Main type options are: D - Disclaimer I - Installation instructions M - Miscellaneous/other S - Shipping/delivery instructions T - Translated name or description A - Alternate/substitute item P - Purchasing instructions |
Sub Type |
Sub type codes are used to identify the language in which the instructions are written, or can have user defined meanings. If used to identify by language, it should relate to the language codes that you create in the Classification Codes File. Product Knowledge screens support sub-type “U” for URL, for the purpose of storing the URL for web-pages related to an item. When the product knowledge screen is displayed in Order Entry, Order Change, Inventory Inquiry, or via the Décor 24 application (on a web-connected PC), the URL may be clicked to open the web page. For more information on this refer to Linking Products to Web Pages via URLS. |
Text |
Type information here. |
Print? |
To specify where this information prints; on the picklist, acknowledgement, invoice, purchase orders. Enter Y to print or N not to print. |
PL |
Pick list. |
ACK |
Acknowledgement or quotations. |
INV |
Invoice to customer. |
P/O |
Purchase order to supplier. |
Col |
Color. You can specify the color for displaying this line on the Order Entry Product Knowledge screen. The color codes control each line on the Order Entry Product Knowledge screen. We recommend that you develop a company-wide system for color-coding information. For example, substitute items could appear in pink, important product disclaimers in red, or installation instructions in white. |
Special Instructions on Printed Documents
If coded to print, the special instructions print below any order line for that product line. Any special instructions with no sub-type for language are printed regardless of the language type for the customer, as coded in the Billto File, Language field. Special instructions coded as a specific sub-type code, such as language, only print for customers with the same language code.
Printing special instructions and product information can greatly enhance the service provided to your customers and help your staff to be more responsive. The following list is a sample of how you can use this Special Instructions system:
Print toxic spill instructions on pick lists below the required items. This is mandated by the Department of Transportation for many chemicals commonly sold in your industry.
Print special picking, handling, and installation instructions below items on pick lists or invoices. These can be entered in any language, and specified for individual customers.
Print legal disclaimers below items that are subject to complaints and claims, such as “Extreme shade variation from samples is possible. Inspect before installation.”
Show the supplier’s item description, in addition to your description, on purchase orders. For importers, this can be a language translation. You can also enter foreign currency unit pricing, which prints on purchase orders.
Show general instructions on all purchase orders, such as “Please include our purchase order number on all correspondence.”
Show general information about items on quotations or order acknowledgements. This can include information such as suggested installation materials and methods, and lead times for special orders.
Print directions for items that can be used as substitutes when you are out of stock. These would be coded not to print, but can be very useful when inquiring.
Reorder Parameters by Warehouse
These parameters override the regular Product Line File reorder control parameters for specific warehouses.
|
Important: If your purchasing is totally centralized (a single warehouse services all other warehouses), then you do not need to make any entries on this screen. The Product Line File Profile screen entries are all you need. Additionally, if the reorder control parameters for any specific warehouse are identical to the product line profile parameters, you do not need to make an entry for that warehouse. On each warehouse entry, enter only the parameters that differ from the Product Line File Profile screen parameters. For example, if the Weeks to Stock for a specific warehouse is different, but the reorder point is the same, enter only the Weeks to Stock. If you leave any field blank on your warehouse entry, the system takes that value from the Product Line File Profile screen. Press Help for online instructions for the window shown above. The entries in this screen are used by the reorder reports.
Field Name |
Description/Instructions |
Warehouse |
Warehouse code, if parameters for that warehouse need to be entered. |
Lead Time (in days) |
Number of days between recognition of a need to purchase and the arrival of goods in the specified warehouse. |
Order Frequency (in days) |
Number of days between actual shipments into the specified warehouses. This indicates how often the product is brought into this warehouse. |
Weeks to Stock |
Amount of stock, expressed in weeks of average demand, below which a reorder should be initiated. |
Reorder Amount (in weeks) |
The amount, expressed in weeks of average demand, that should be reordered when the reorder point is reached. |
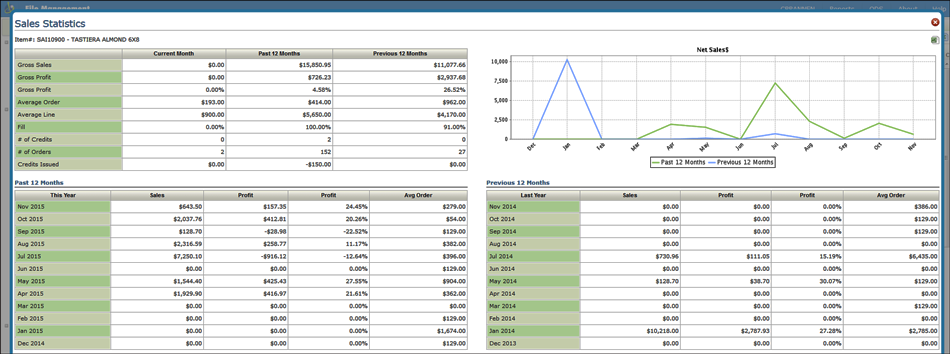
The information displayed is the same sales statistic information displayed when using the F4 function on the green screen.
Granting Access to the Sales Statistics
As with most Navigator Functionality, permission has to be granted at one of the following levels:
Global - via menu option NAV 1
Authority Class - via menu option NAV 2
User - via menu option NAV 5
Access one of the above Navigator options (NAV 1, 2 or 5) and select F10 - Navigator Options/Permissions.
Note: At the Authority Class (NAV 2) and User (NAV 5) levels, you need to enter a “W” in the appropriate Opt field.
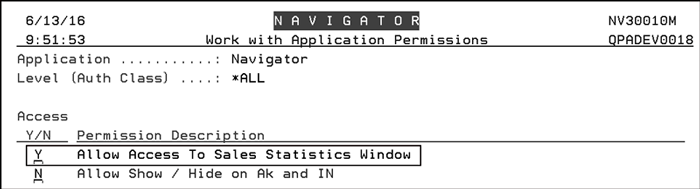
Enter a “Y” to allow access to the Sales Statistics.
Viewing Sales Statistics in Navigator
Select Sales Statistics from the Option Drop down menu. The Sales Statistics window appears.
Field Name |
Description/Instructions |
Gross Sales |
Includes the total amount billed on invoices and credit memos, excluding tax, freight, and discount/handling charges, which appear separately at the bottom of the invoice or credit memo. Miscellaneous sales (entered in miscellaneous F6 lines on Order Entry) are included or excluded based on a company setting that is set when the system is installed. |
Gross Profit $ |
Gross profit; gross sales (as defined above) minus the cost of goods sold, as it appears on the invoice registers. |
Gross Profit % |
Gross profit percentage; gross profit divided by gross sales. |
Average Order |
The total amount ordered divided by the total number of orders. Order size does not relate to Gross Sale $, unless all of the orders were invoiced at the same time. This screen could show an average order figure and zero for gross sales if the orders were not invoiced. This figure represents the size of orders, not the size of shipments, which might be, for example, out-of-stock or split deliveries. |
Average Line |
The total amount ordered divided by the total number of order line items. |
Fill% |
Dollar amount shipped divided by the dollar amount ordered. This shows how well you fill the orders you take. Fill% is calculated at invoice time, by taking the amount shipped and dividing it by the amount on the order, not including back orders. A Fill% of 100% means you shipped everything that was ordered. Over-shipments are calculated as complete shipments. Fill% can never exceed 100%. To increase the scope of the Fill% figure, you can enter orders for out of stock goods. Normally, you tell the customer you are out of stock and not enter an order that you could not fill. However, if you enter the order and invoice it for zero shipped, you’ll reflect the missed sales in ordering statistics and Fill%, which represent the true demand for each item. |
# of credits |
Number of credit memos issued, including debit invoices that include a credit, such as for a material exchange. |
# of orders |
Number of orders issued. Orders are only considered issued if they are printed or processed. Temporary holds of inventory are not counted as orders until processed as orders. Don’t confuse number of orders with number of invoices. |
# of lines |
Number of order lines issued. |
Cred Issued |
Dollar amount of credit issued, including credit memos and credit lines included within debit invoices. Credit lines can be entered in debit invoices when customers are exchanging material. |
Green Screen Product Line (FIL 12)
Product Line Statistics By Warehouse File - FIL 21
Product Knowledge Mass Update - SYS 920
Product Line Statistics Screen (related to Product Budget Reports) - SYS 918
Reports (off master reports menu option RPT)
By Product Line - RPT 59
Print Product Line Forecast Report - RPT 119
Print Product By Warehouse By Month Spreadsheets - RPT 123
List Product Line File - RPT 162
Product Sales Reports (by Item or Customer) RPT 353
Special Order Product Sales Reports - RPT 355
By Product Line - RPT 409
Rank Product Lines - RPT 459
Print Product Line Forecast Reports - RPT 507
Search Product Line File - FSR 12
How to delete price, cost, packaging, salesperson, manufacturer and product line files
Is there a report by customer for what products were purchased?