Categories and Classifications
These three-character codes represent chain stores and other multi-location accounts, or groups of accounts. For example, JCP for JC Penny. Assign chain codes to all account numbers in each chain using the Chain field in the Billto File.
You can use this feature creatively to link customers that are not technically considered chains. When you create a chain, you can analyze sales for the chain, as well as the individual customers included in the chain.
The Billto Count column shows how many Billto accounts are assigned to a chain code.
This one-character code represents the relative value class of each item. Suggested codes are:
- H - High end or luxury items
- M - Medium level items
- L - Low level/commodity products
Each item can be assigned a commodity level code in the Item File. You can take a more detailed approach to the commodity level and assign codes that represent specific price ranges. For example, 1 equals up to 1.99 or 2 equals up to 2.99. This field is designated to help you analyze the levels of the market place with which you are the most and least successful. You can also run many sales reports such as Customer by Commodity Level.
These one-character codes represent types of credits or reasons for credits that are used by Order Entry and Invoicing. You must enter a credit code whenever a credit is entered. Suggested codes include:
- D - Damaged or defective material
- E - Exchange of material
- K - Keypunch error
- P - Pricing error
- Q - Quantity overestimated, excess returned
- W - Warehouse error, wrong item
You can also reserve a few codes for identifying special types of sales in Order Entry. For example, code Z could indicate low margin blow out sale or code X could indicate special spiff sale.
These codes can be reported on using the X by Y Sales Analysis Reports. These codes can also trigger special sales commission rates. For example, code X can trigger a 5% of sales commission.
Customer types are entered for each customer in the Billto file. When an order is entered, the order entry program gets the customer type from the Billto account.
If the customer is flagged as a retail customer, Order Entry displays the Retail Customer File, allowing you to select from or add to the list of retail customers.
This three-character code represents major product displays and sample sets that are provided by your company or your suppliers, and used by your customers to promote your products. This enables you to track which customers have which displays or samples, and to analyze sales for customers with and without these displays. You can code up to 20 displays per customer. Special pricing can be assigned to a display type which affects all customers assigned with that display type code.
This three-character code is defined in this file and then assigned in the Price File. Each price class can be entered into a single end user category. The end user category is a category for your customers, not for your internal statistics. It is used for the following functions:
Customers who access your system via a product such as Decor 24 can only see the items and prices that relate to the end user categories to which they are assigned.
Customer Price Lists can use the end user category as a parameter. You can request price lists for specified end user categories. They can also be sorted by the end user category.
By omitting a price class record from all end user categories, you can block customers from seeÂing that record on price lists and dial-in screens. This process can be useful for samples, off goods, and other records you want omitted from your customer price lists and screens. Enter only the end user category in price records that you want to include on price lists or customer dial-in screens. End user categories need only to be entered on the LP records of the Price File.
Because the end user category is not intended for sales analysis, it does not build online statistics.
Freight classes require special information primarily for use on bills of lading.
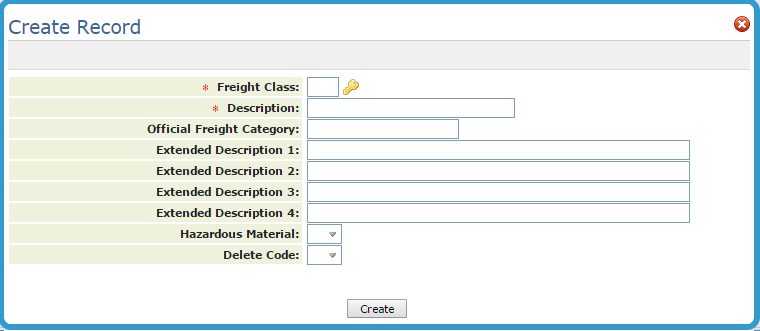
| Field Name | Description/Instructions |
| Freight Class | The freight class code as entered in the Entry screen. |
| Description | The description of the freight class. |
| Official Freight Category | The official or standard freight class number, code, or abbreviation to print on bills of lading. This field is only applicable to bills of lading and certain EDI transactions. |
| Extended Descr. |
Enter extended description or instructions, if needed, to print on all bills of lading for products assigned to this freight class. Extended descriptions are printed on bills of lading. Freight classes are assigned to items in the Item File. Freight class information only appears on bills of lading and in EDI transmissions. You may be required to maintain information such as hazardous goods warnings for each freight class based on government regulations. |
| Hazardous Material | Enter Y if the maintain information such as hazardous goods warnings for each freight class based upon government regulations. Enter N if not government regulated as hazardous. An entry of Y causes the hazardous goods message to appear on Bills of Lading and to appear before any non-hazardous freight classes. |
These one-character codes represent the FOB and shipping freight terms. This code is used in Order Entry. Default FOB codes can be entered into the Billto File and into the Work Station Control Panels. Suggested codes include:
- C - Customer's warehouse
- F - Factory
- P - Port of entry
- W - Our warehouse
- 1 - Freight collect
- 2 - Freight prepaid
- 3 - Freight bill to follow
We suggest that you abbreviate these descriptions as much as possible. Only the first 14 characters can fit on most documents. Always use the FOB code to note whether freight is prepaid or collected on common carrier shipments.
These one-character codes represent languages in which your special instructions for items and customers are entered or printed. A code is assigned to customers using the Language field in the Billto File. Each customer can be coded as speaking a language which, when applicable, will be chosen when information entered in multiple languages print on pick lists, invoices, and so on. Create language codes only if you will enter information in more than one language. Suggested codes include:
- E - English
- F - French
- I - Italian
- S - Spanish
This three-character code groups or categorizes customers for a variety of purposes. Usually, marketing program codes are used to identify a customer as belonging to a group of customers for promotional or marketing purposes. For example, marketing program H13 could be assigned to all customers participating in the Hawaii 2013 Promotional Contest. Marketing programs are assigned from the Billto File. You can assign up to 20 different marketing programs to each customer. Special pricing can be assigned to a marketing program.
This two-character code represents the operators on your system. These codes are assigned to each order, and enable tracking of activity by operator.
These two-character codes represent different price lists you maintain on the system. For example, you could use DL for dealer price list or BL for builders price list. Avoid using the following price list codes when creating price list codes, because they represent pre-programmed pricing options on the system that can be specified where ever a price list can be specified.
- SC - Standard cost (landed cost includes freight)
- LC - Last cost (the landed cost of the last receipt per SKU and warehouse)
- AC - Average cost
- BC - Standard base cost (excludes freight)
- LP - List Price. This code must be created on all systems and is set up by KerridgeNC when systems are installed.
- L0 - L9 are reserved by List Price system.
- 99 - Restricted from buying. Assigning this code, for all or a specified product, restricts the cusÂtomer from buying those products. When this code is assigned, the Order Entry program displays this message: Customer cannot buy this product.
Examples of price list codes you can create:
- C1 - Contractor level 1 price list
- C2 - Contractor level 2 price list
- KD - Key dealers price list
- NC - North Carolina price list
The Currency Code column shows the currency tied to the price list code. In order for the system to convert currencies, the code entered must be included in the Currency Code/Exch Rate Table. The default currency code is for display purposes only in the Price File. All prices are still always stored in your home currency.
These one-character codes represent the method used to determine pricing of a line of an order. Every line entered and priced in order entry is assigned a pricing method code to show how the pricing was calculated. Example pricing methods are:
- C - Customer exception pricing (customer has a special price list assigned for a given product.) Customer exceptions are entered in the Pricing Exception screen of the Billto File.
- F - Fixed pricing (This is set up in the Promotional Price File where a customer can be assigned a price that will override all other prices.)
- H - In-house promotion (promotional price sponsored in-house)
- M - Manufacturer-based promotion (promotional price sponsored by the manufacturer)
- R - Regular pricing (normal pricing for a given customer or product)
- S - Special price from the Customer Special Price File.
- X - Overridden pricing (price overridden by order entry operator). As an example, you can enter PM as the Category and then X as the class code. A Sales Analysis screen appears with informaÂtion on all your price override transactions.
- Z - Zero Pricing (Manufacturer Components)
A pricing method code is assigned automatically to every line of each order and invoice. The system tracks the overall profitability of each of these methods of pricing.
These two-character codes are used by invoicing to group items together to determine quantity break pricing. Examples of Quantity Break Codes:
- T1 - Tile group 1
- T2 - Tile group 2
- A1 - Accessories group 1
These two-character codes represent geographic regions in which your customers are located. These codes are separate from, and in addition to, codes for state and country, and from zip codes, and county numbers. A region code can be assigned to each customer in the Billto File. Region codes can be used for sales analysis, mailing lists, and for assigning promotional pricing.
These three-character codes are used to group items together for reordering. This code can be assigned to group items together on reorder reports. A reorder/buying category can represent the group of products such as DCT = Domestic Ceramic Tile or the buyer, such as JOE = Joe Smith. Reorder/buying categories are assigned to product lines using the Product Line File maintenance program.
Restriction codes are used primarily for pricing. Some examples are
- R - Roll price (rolled goods only)
- C - Cut price (rolled goods only)
- B - Roll balance (rolled goods only). Translates to R for pricing and statistics.
- M - Management authorized sale price or mid-price (any goods)
- T - Truckload Pricing
- L - LTL (less than truckload) pricing
- P - pallet pricing
- U - unit pricing (used for other miscellaneous unit pricing such s container pricing
Sales analysis statistics are automatically gathered for these codes, so you can monitor roll vs. cut business, and your use of the management authorized sale price feature. These codes are used in the Order Entry system to retrieve prices. If you use the 3 price option (roll/cut/balance) for rolled goods, then M is the mid/balance price.
These two-character codes represent shipping methods. These codes are used in Order Entry. They also display throughout the shipping and credit processes. Default ship via codes can be entered into the Billto File and into the Work Station Control Panels. Suggested entries include:
- CC - Common carrier
- CF - Consolidated freight
- OT - Our truck
- PS - Pick up showroom
- PW - Pick up warehouse
- RO - Rush order
- UP - UPS Regular
- WC - Will call
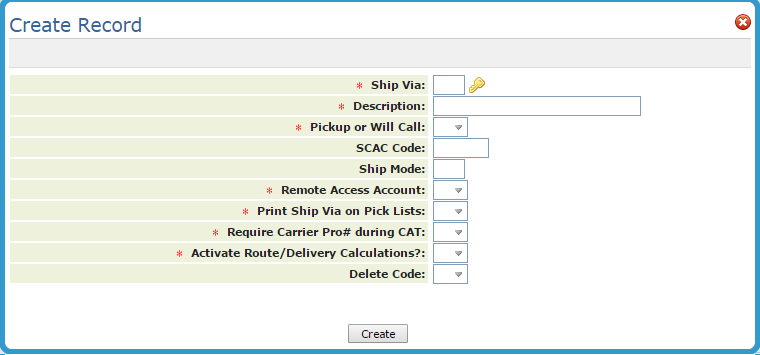
| Field Name | Description/Instructions |
| Ship Via | The ship via code as specified on the Classification Codes Entry screen. |
| Description | The description related to the ship via code. |
| Pick Up or Will Call | Enter Y if the ship via code represents a pick up or will call, as opposed to a delivery or shipment. This field is used in order entry and invoicing whenever tax on a will call or pick up is different than if the goods were shipped. Otherwise, enter N. |
| SCAC Code | The standard assigned code for a shipper or carrier. It is required for many EDI transmissions, including advanced shipment notices which inform your customers and manufacturers of the contents of a shipment. |
| Ship Mode | Used in EDI, this standard code identifies the mode of transportation used by a carrier. For example, there are codes representing flat bed trucks, van, shipping container, and so on. Enter into this field only for carriers if you use EDI. |
| Remote-Access Account | Entering a Y in this field allows this ship via to be listed on remote access order entry systems, such as Decor 24. Enter N in this field if your remote access customers should not see this ship via as a valid choice. |
| Print Ship Via on Pick Lists | Enter a Y in this field to suppress the printing of a shipto address on pick lists whenever this ship via code is used. In place of the shipto address, the ship via description prints. This is meant primarily for will-calls and pickups, if you are concerned about accidental shipments of goods to be picked up. |
| Require Carrier Pro# during CAT: | If you flag this field with Y, when you use the Close-A-Truck (CAT) program, you will be prompted to enter the carrier pro number for the carrier. If this ship via code uses one of your own trucks, enter an N in this field. For shipments that use your own trucks, you will normally use a packing list, and not need to capture a PRO#. However, if the ship via code represents an outside carrier, you should enter Y to trigger the prompt to capture Pro#s during the Close-A-Truck (CAT) process. Note: In order for a bar code to print on a Bill of Lading, you must specify the correct format. |
| Activate Route/Delivery Calculations |
If you flag this field with Y, when you use the Close-A-Truck (CAT) program, you will be prompted to enter the carrier pro number for the carrier. If this ship via code uses one of your own trucks, enter an N in this field. For shipments that use your own trucks, you will normally use a packing list, and not need to capture a PRO#. However, if the ship via code represents an outside carrier, you should enter Y to trigger the prompt to capture Pro#s during the Close-A-Truck (CAT) process. In order for a bar code to print on a Bill of Lading, you must specify the correct format. |
These codes define the type of transactions available to the Order Entry, Sales Analysis, and Pricing modules. Some of these codes are included when your system is initially installed. They include:
- C - Intercompany sales
- D - Direct shipments
- I - Sales from inventory
- S - Special orders
Sales statistics are automatically gathered for each of these codes. Different prices and costs can be maintained based on transaction type.
This two-character code is used to identify trim items. Trim is defined as support products or products sold as accessories to your main products. They would include reducer strips and moldings for wood, and bullnoses and out corners for ceramic tile. Enter a trim class only for trim items. Optionally, you can code setting materials, polishes, samples, tools, and so on as trim. If you do not need to sub-categorize your trim items, you may simply enter a single trim class code of TR for trim, and enter that code for all trim items. Many reports on the system have an option to include or omit trim items. We especially recommend the use of this feature for ceramic tile. For wall tile lines, classify your trims into categories such as surface, mud, bullnose, or angles to facilitate flexible stock reporting. These codes are assigned to items in the Item File.
Although this screen defines a truck route, you can use a common carrier or external shipping company to deliver your goods. In that case, your truck route represents a carrier as well as a route. If this is the case, and you are using EDI, you might be required to transmit the carrier's SCAC code and Ship Mode code. The SCAC and Ship Mode codes can be stored on this screen for all your routes that utilize common carriers.
This one-character code represents the durability rating of each product. Usually, each industry will have standard codes such as:
- 1 - Light residential use
- 2 - Heavy residential use
- 3 - Light commercial use
- 4 - Heavy commercial use
You can enter industry standard codes or create your own. One of these codes should be assigned to each applicable item using the Wear Code field in the Item Master File.
This two-character code represents the workstation IDs on your system. These codes are assigned automatically to each order, and enable tracking of activity by terminal.
